Neurodegenerative disorders impact hundreds of millions globally, imposing immense medical and financial burdens on patients, their families, and society. NeuExcell is committed to advancing its ATN ASTROCYTES TO NEURONSTM platform technology to develop therapies that offer patients the potential for transformative improvement.
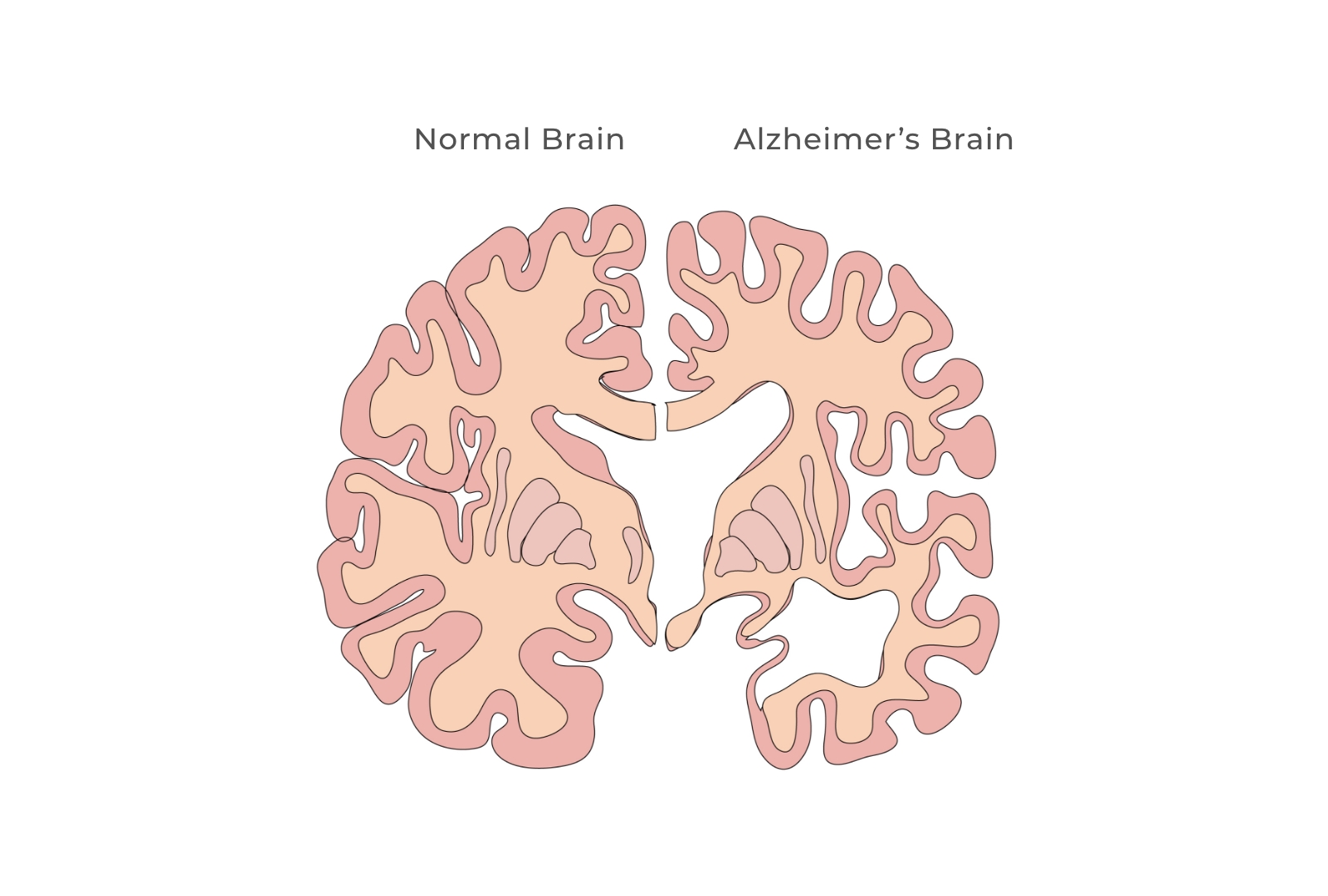
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia. Patients with AD typically experience memory loss in the early stages of the disease, followed by a progressive decline in self-care abilities, often accompanied by behavioral and neuropsychiatric symptoms. The etiology of AD remains poorly understood, early clinical diagnosis is challenging, and there are currently no effective disease-modifying treatments. AD is characterized by extensive neuronal loss, particularly in brain regions responsible for learning, memory, and higher cognitive functions, such as the hippocampus and cerebral cortex. By expressing a single transcription factor, NeuroD1, astrocytes can be directly converted into neurons in the cortex or hippocampus of AD model mice as well as in non-human primate AD models. These newly generated neurons integrate into existing neural circuits and exhibit functional activity. This approach represents a promising new therapeutic strategy for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Stroke is the leading cause of long-term disability in the US, afflicting nearly 800,000 people each year, with a total of seven million stroke survivors. It can cause the loss of a vast number of neurons in the brain, leading to serious impairments such as limb paralysis and language difficulties. The irreversible loss of neurons remains a major challenge, limiting effective treatment options and hindering functional recovery. Current standard treatments must be administered within hours of a stroke to minimize neural damage. In contrast, our technology offers a significantly extended treatment window-ranging from days to weeks, or even months post-stroke. Developed from our ATN ASTROCYTES TO NEURONS (TM) platform, our in situ neuroregeneration technology enables the repair of damaged neural tissue. This approach has demonstrated remarkable tissue repair and functional recovery in a non-human primate stroke model. NeuExcell's neuroregeneration technology brings new hope for stroke patients, offering the potential for meaningful functional recovery.
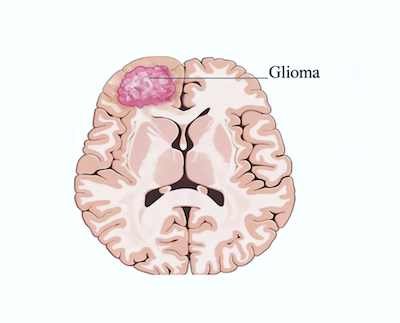
Gliomas are the most common malignant primary brain tumors and arise from glial cells in the central nervous system. Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most aggressive and lethal form of glioma, characterized by rapid tumor growth, diffuse invasion into surrounding brain tissue, and resistance to existing therapies. Standard treatment includes surgical resection followed by radiation and chemotherapy; however, tumor recurrence is almost inevitable. Median overall survival remains 14-18 months, and long-term survival rate remains <10%. GBM causes substantial neurological impairment, including cognitive dysfunction, seizures, and loss of motor function, leading to severe declines in quality of life. The aggressive nature of the disease and limited therapeutic progress over past decades underscore a significant unmet medical need and the urgency for innovative treatment strategies. The ATNTM technology reprograms tumor cells into non-dividing neurons or induces cell apoptosis, representing a novel therapeutic paradigm.
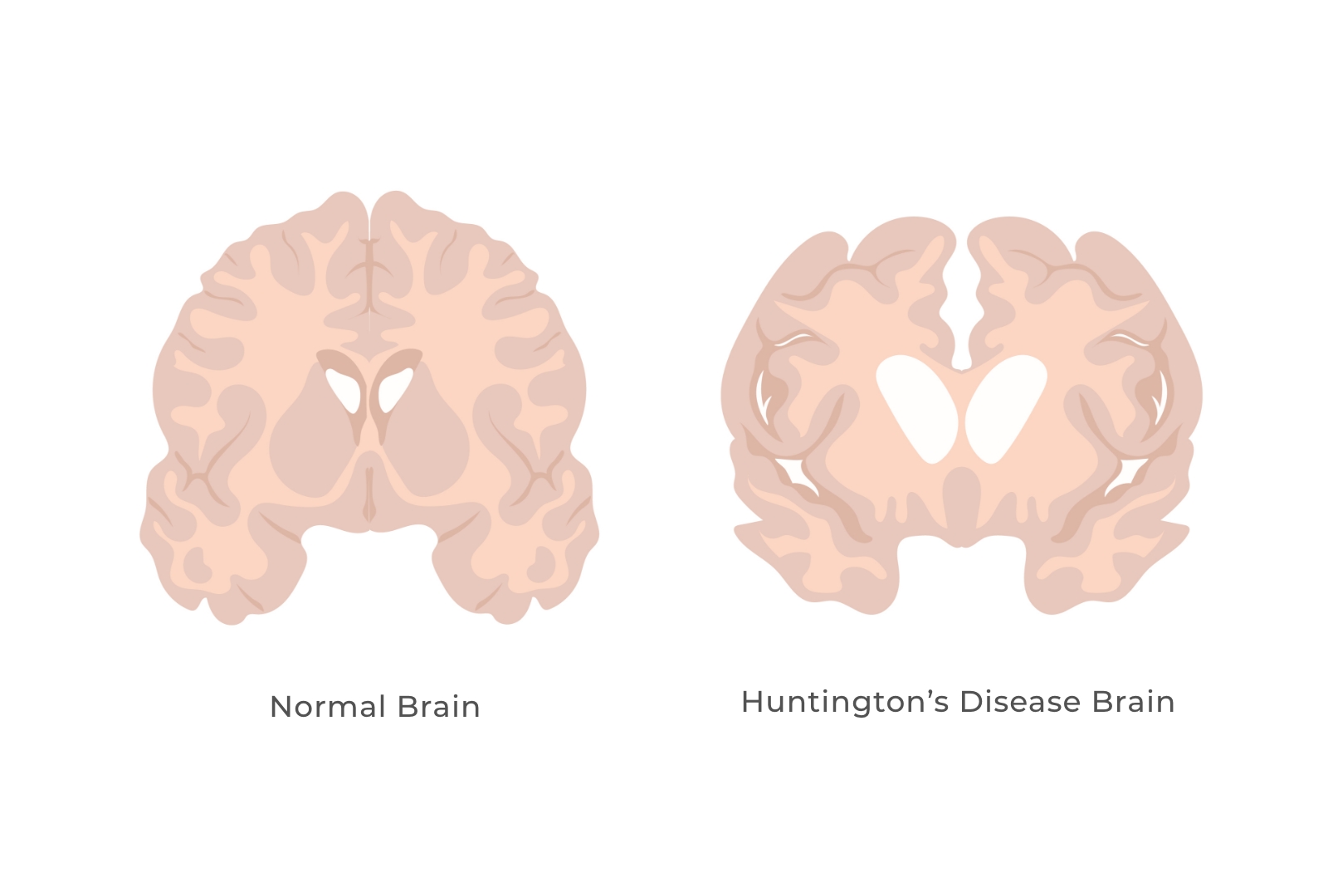
HD is a fatal rare inherited genetic disorder with severe neuron death in the striatum of the brain. HD patients suffer from motor, cognitive and emotional impairments and condition deteriate over the course of 10 to 25 years. Current limited therapies can only relieve chorea symptoms, and patients are ultimately left without a cure. Our direct conversion of astrocytes to neurons (AtN) can regenerate neurons to repair the neural tissue. In HD model mice the AtN conversion can rescue the brain atrophy, improve motor function and significantly prolong the lives of HD mice.

ALS is a fatal rare progressive neurodegenerative disease caused by motor neurons deterioration and death. ALS patients suffer from progressively worsening skeletal muscle weakness and stiffness and at the end losing ability to move, speak, eat, or even breathe. The core pathological change of ALS is the death of upper and lower motor neurons in the brain and spinal cord, and there is currently no way to reverse its progression. At present, the etiology is not clear, there is no effective treatment, and the median survival time is only 3-5 years after diagnosis. In situ neuroregeneration technology can replenish the lost neurons through convert endogenous astrocytes to neurons (AtN) through expressing neural transcription factors, which offers tremendous therapeutic potential for ALS.
In situ neuroregeneration technology can also be applied to a variety of other neurological diseases, such as Parkinson's disease, traumatic brain injury, spinal cord injury, brain tumors, and ophthalmic diseases. These indications are currently in the early discovery phase but will continue to develop as we deepen our understanding of developmental biology, NeuroD1 and other neural transcriptions, and our AtN platform. These programs continue to grow and will fuel our future pipeline.